正则表达式&各类函数
本文最后更新于:2024年1月4日 晚上
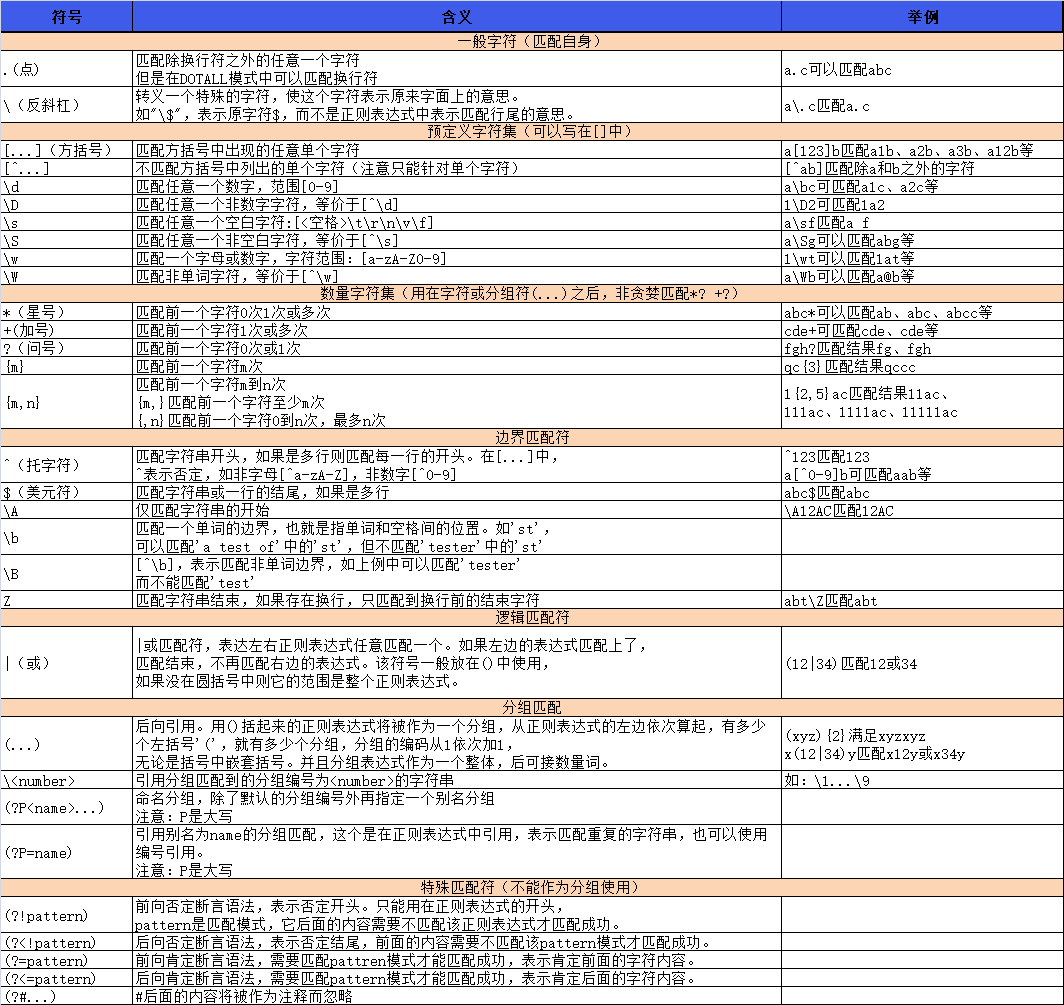
正则表达式
由于正则表达式通常包含反斜杠等特殊字符,所以我们最好使用原始字符串来表示他们。如:r’,等价于’\d’,表示匹配一个数字。
Python正则表达式中,数量词默认都是贪婪的,它们会尽力尽可能多的去匹配满足的字符,但是如果我们在后面加上问号“?”,就可以屏蔽贪婪模式,表示匹配尽可能少的字符。 如字符串:“xyyyyzs”,使用正则“xy*”,就会得到“xyyyy”;如果使用正则“xy*?”,将只会匹配“x”

1、re.compile
- re.compile(pattern, flags=0)
- a=re.compile(r'hello')
将正则表达式编译成对象a(相当于模版,这样不会对每个要使用正则的对象都输入一遍r'hello',而是直接用对象a及其方法来引用:a.search("hello
world!"),一处编译,多处复用。
- pattern = re.compile(r'hello') pattern.match('hello world!') 以上两句等价于re.match(r”hello”,”hello world!”)
- 第二个参数flag是匹配模式,取值可以使用按位或运算符==“|”表示同时生效==,比如re.I | re.M(忽略大小写,换行匹配)。
- re.compile('pattern', re.I | re.M)它等价于: re.compile('(?im)pattern')
pattern对象下有哪些属性和方法:
>>> pattern=re.compile(r"hello")
>>> dir(pattern)
['findall', 'finditer', 'flags', 'groupindex', 'groups', 'match', 'pattern', 'scanner', 'search', 'split', 'sub', 'subn']
| 表示同时生效
re.I 忽略大小写
re.L 表示特殊字符集 \w, \W, \b, \B, \s, \S 依赖于当前环境
re.M 多行模式
re.S 即为 . 并且包括换行符在内的任意字符(. 不包括换行符)
re.U 表示特殊字符集 \w, \W, \b, \B, \d, \D, \s, \S 依赖于 Unicode 字符属性数据库
re.X 为了增加可读性,忽略空格和 # 后面的注释2、pattern.match()
- group() ——返回匹配结果
- string:被匹配的字符串 pos:匹配的起始位置,可选,默认为0 endpos:匹配的结束位置,可选,默认为len(string)
- re.match方法从头开始匹配,匹配不到就返回None
- pattern.match和re.match的区别是pattern.match可以指定匹配的起始位置,而不用对象直接match无法指定匹配位置,默认匹配全部
>>> import re >>> pattern=re.compile(r"\w+") >>> pattern.match("qwer123",0,2).group() 'qw' >>> pattern.match("qwer123",0,3).group() 'qwe'
re.match()
- 该函数的作用是尝试从字符串string的起始位置开始匹配一个模式pattern,如果匹配成功返回一个匹配成功后的Match对象,否则返回None。
参数说明: pattern:匹配的正则表达式 string:要匹配的字符串
flags:标志位,用于控制正则表达式的匹配方式。如是否区分大小写、是否多行匹配等。
例子:
>>> re.match(r"\w+","avde").group() 'avde'
re.match()方法与pattern.match()方法区别:
re.match()不能指定匹配的区间pos和endpos两个参数,pattern.match可以。
3、pattern. search()
该方法的作用是在string[pos, endpos]区间从pos下标处开始匹配pattern,如果匹配成功,返回匹配成功的Match对象; 如果没有匹配成功,则将pos加1后重新尝试匹配,直到pos=endpos时仍无法匹配则返回None。 参数说明: string:被匹配的字符串 pos:匹配的起始位置,可选,默认为0 endpos:匹配的结束位置,可选,默认为len(string) 也就是说如果不指定pos和endpos这两个参数的话,该方法会扫描整个字符串。 - 注意,如果string中存在多个pattern子串,只返回第一个
例子:
>>> pattern=re.compile("\d+\w*")
>>> pattern.search("12abc123ABc123",0,10).group()
'12abc123AB'
>>> pattern.search("12abc123ABc123",0,9).group()
'12abc123A're.search()不能指定匹配的区间pos和endpos两个参数。
re.match与re.search的区别:
re.match只匹配字符串的开始,如果字符串开始不符合正则表达 式,则匹配失败,并返回None; 而re.search匹配整个字符串,直到找到一个匹配。 - 所以,如果你想要从字符串的一开始就进行匹配或匹配整个字符串的话就使用match。它更加快速,否则请使用search。
# example code:
string_with_newlines = """something
someotherthing"""
import re
print re.match('some', string_with_newlines) # matches
print re.match('someother', string_with_newlines) # won't match
print re.match('^someother', string_with_newlines, re.MULTILINE) # also won't match
print re.search('someother', string_with_newlines) # finds something
print re.search('^someother', string_with_newlines, re.MULTILINE) # also finds something,re.MULTILINE 匹配多行模式。
m = re.compile('thing$', re.MULTILINE)
print m.match(string_with_newlines) # no match
print m.match(string_with_newlines, pos=4) # matches
print m.search(string_with_newlines,re.MULTILINE) # also matches- re.match() 从第一个字符开始找, 如果第一个字符就不匹配就返回None, 不继续匹配. 用于判断字符串开头或整个字符串是否匹配,速度快.
- re.search() 会整个字符串查找,直到找到一个匹配。
- re.MULTILINE 匹配多行模式
4、findall
re.findall(pattern, string[, flags])
返回string中所有与pattern相匹配的全部字串,返回形式为数组。 ### 5、finditer re.finditer(pattern, string[, flags]) 返回string中所有与pattern相匹配的全部字串,返回形式为迭代器。
group(). groups()的区别
>>> import re
>>> s = '23432werwre2342werwrew'
>>> p = r'(\d*)([a-zA-Z]*)'
>>> m = re.match(p,s)
>>> m.group()
'23432werwre'
>>> m.group(0)
'23432werwre'
>>> m.group(1)
'23432'
>>> m.group(2)
'werwre'
>>> m.groups()
('23432', 'werwre')
>>> m = re.findall(p,s)
>>> m
[('23432', 'werwre'), ('2342', 'werwrew'), ('', '')]
>>> p=r'(\d+)'
>>> m=re.match(p,s)
>>> m.group()
'23432'
>>> m.group(0)
'23432'
>>> m.group(1)
'23432'
>>> m.groups()
('23432',)
>>> m=re.findall(p,s)
>>> m
['23432', '2342']正则表达式的\1
正则表达式中 ‘\1’ 匹配的是 字符 ‘\1’ 。 (因为 ‘’ 匹配字符 ‘’ ) ‘\2’ 匹配的是 字符 ‘\2’
正则表达式中的小括号"()"。是代表分组的意思。 如果再其后面出现\1则是代表与第一个小括号中要匹配的内容相同。
注意:\1必须与小括号配合使用
‘\1’ 匹配的是 所获取的第1个()匹配的引用。例如,’(\1’ 匹配两个连续数字字符。如33aa 中的33 ‘\2’ 匹配的是 所获取的第2个()匹配的引用。 例如,’((a)\1’ 匹配第一是数字第二是字符a,第三\1必须匹配第一个一样的数字重复一次,也就是被引用一次。如9a9 被匹配,但9a8不会被匹配,因为第三位的\1必须是9才可以, ‘((a)\2’ 匹配第一个是一个数字,第二个是a,第三个\2必须是第二组()中匹配一样的,如,8aa被匹配,但8ab,7a7不会被匹配,第三位必须是第二组字符的复制版,也是就引用第二组正则的匹配内容。
正则表达式手册
https://tool.oschina.net/uploads/apidocs/jquery/regexp.html
empty
当 var 存在,并且是一个非空非零的值时返回 FALSE 否则返回 TRUE。
==为空/0返回true !!==
以下的变量会被认为是空的:
"" (空字符串)
0 (作为整数的0)
0.0 (作为浮点数的0)
"0" (作为字符串的0)
NULL
FALSE
array() (一个空数组)
$var; (一个声明了,但是没有值的变量)博客文章采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处,有疑问欢迎联系:)